[Quipu Issue Paper] Genome Annotation Ⅲ- 유전체 정렬(Genome alignment)
- Posted at 2010/03/17 09:31
- Filed under 생물정보
연재 순서
1. Assembly
2. Variation study
3. Expression study
4. Epigenomics
5. Genome Annotation
6. Next Generation Bioinformatics
7. Data Management for web 2.0 Era
8. Semantic Network for Integrated Biology Data
9. Gene Network Discovery by Text-mining
10. Centralization for High-throughput Data Analysis
이번 연재에서는 유전자 모델을 얻는 과정으로 서열 정보를 이용하여 유전체를 정렬(Genome alignment)하는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
B-2. 유전체 정렬(Genome alignment)
유전체 상에서 유전자의 위치 및 구조 정보를 파악하는데 가장 중요한 정보를 제공하는 것이 mRNA를 비롯한 실제 서열정보이다. 유전체 프로젝트를 수행하면서 Full-length mRNA 시퀀싱을 함께 진행하는 이유라고 할 수 있다. 그 외 단백질과 ESTs 서열도 유전자 구조 정보를 제공하는 좋은 재료이다[11]. 최대한 많은 양의 실제 데이터(evidence data)를 확보하여 유전체 서열과의 유사성(similarity)을 조사하고 그 위치를 파악한다. DNA 서열의 경우 BLAT[13], Sim4[14], GMAP[16], AAT[15]가 주로 이용되고, 단백질 서열의 경우 BLAST와 wise2 package에 존재하는 Genewise[17]를 이용한다. 유전체 서열이 매우 크므로 일차적으로 빠르게 매핑할 수 있는 BLAT이나 BLAST 등으로 대략의 위치를 설정하고 그 외 다른 프로그램을 이용하여 좀 더 정교한 2차 매핑을 수행하는 경우도 있다.
이때, 서열상의 유사성에 의해 유전자 모델(Evidenced Gene Model)이 결정되므로 HSP length, coverage, identity와 같은 파라미터 조건을 엄격하게 설정하여 정확한 Evidenced Gene Model(EGM)을 만드는 것이 일반적이다. 또한 언급한 대부분의 프로그램은 모두 exon/intron 신호를 인지하며 local alignment을 수행하고 있어 intron이 존재하는 유전체 서열에 매핑 하기에 모두 적절한 프로그램이다.
특히 genewise의 경우 매핑과 동시에 가능한 유전자 모델을 제시한다. 따라서 유전체 서열과 유연 관계가 가까운 이종의 단백질 서열을 매핑 하여도 좋은 결과를 얻을 수 있다. 다만, 이후 진행되는 consensus gene model을 만들 때 score를 적절히 조절 해야만 한다. 다양한 프로그램을 통해 얻어진 유전자 모델 정보는 모두 동일한 형태의 파일 포맷을 유지하는 것이 좋다. 대부분의 프로그램이 공통적으로 지원하는 파일 형태는 GFF3 포맷이다(그림 4).
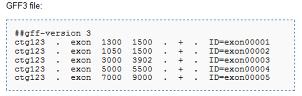
seqld/source(tool name)/type/start/end/score/strand/phase/attributes
다음 연재에서는 앞서 설명한 유전자 예측 프로그램과 단백질 서열을 유전체에 매핑하여 얻어진 Gene Model을 결합하는 유전체 모델의 결합(Gene model merging)에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 많은 관심 부탁드립니다.
참고문헌
1. Lowe, T.M. and Eddy, S.R. (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 955-964.
2. Lewis SE, et al. (2002). Apollo: a sequence annotation editor. Genome Biology. 12, research0082
3. Noh SJ, Lee K, Paik H, Hur CG. (2006) TISA: tissue-specific alternative splicing in human and mouse genes. DNA Res. 13, 229-243
4. Stanke M, Schoffmann O, Morgenstern B, Waack S. (2006) Gene prediction in eukaryotes with a generalized hidden Markov model that uses hints from external
sources. BMC Bioinformatics. 7, 62.
5. Burge, C. and Karlin, S. (1997) Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 268, 78-94.
6. Salamov AA, Solovyev VV. (2000) Ab initio gene finding in Drosophila genomic DNA. Genome Res. 10, 516–522.
7. Majoros, W.H., Pertea, M., and Salzberg, S.L. TigrScan and GlimmerHMM: two open-source ab initio eukaryotic gene-finders Bioinformatics 20, 2878-2879.
8. G. Parra, E. Blanco, and R. Guigó, (2000) Geneid in Drosophila Genome Research 4, 511-515.
9. Haas BJ, Salzberg SL, Zhu W, Pertea M, Allen JE, Orvis J, White O, Buell CR, Wortman JR. (2008) Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using
EVidenceModeler and the Program to Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biology 9, R7
10. Korf I. (2004) Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinformatics. 5, 59.
11. Kan, Z., Rouchka, E.C., Gish, W., and States, D. 2001, Gene structure prediction and AS analysis using genomically aligned ESTs, Genome Res. 11, 889–900.
12. Eyras, E., Caccamo, M., Curwen, V., and Clamp, M. 2004, ESTGenes: AS from ESTs in Ensembl, Genome Res. 14, 976–987.
13. Kent, W.J. 2002, BLAT-The BLAST-Like Alignment Tool, Genome Res. 12, 565–664.
14. Florea, L., Hartzell, G., Zhang, Z., Rubin, G.M., Miller, W. 1998, Computer program for aligning a cDNA sequence with a genomic DNA sequence, Genome Res. 8,
967–974.
15. Huang X, Adams MD, Zhou H, Kerlavage AR. (1997) A tool for analyzing and annotating genomic sequences. Genomics. 46, 37–45.
16. Wu TD, Watanabe CK. (2005) GMAP: a genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatics. 21, 1859–1875.
17. Birney E, Clamp M, Durbin R. (2004) GeneWise and Genomewise. Genome Res. 14, 988–995.
Posted by 人Co
- Tag
- AAT, BLAST, BLAT, EGM, Evidenced Gene Model, exon, Genewise, Genome alignment, GFF3, GMAP, insilicogen, intron, NGS, Sim4, 유전체 정렬, 인실리코젠
- Response
- No Trackback , No Comment
- RSS :
- https://post-blog.insilicogen.com/blog/rss/response/59


